9th Computer Notes
Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Computer

Write short answers to the following questions
i. Describe Napier’s Bone and Slide Rule.
Ans: Napier’s Bone:
John Napier a Scottish mathematician, invented a calculating device called Napier’s Bone in 1614. It consisted of a wooden box with rotating cylinders. Each cylinder had digits from 0 to 9. The device could multiply, divide, and find square roots of numbers using simple addition and subtraction.

Slide Rule:
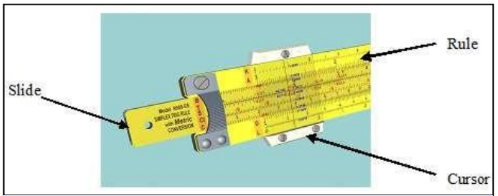
Based on the idea of the logarithm, English mathematician, William Oughtred developed a device called Slide Rule in the 1920s. It was very useful for solving problems that involved multiplications and divisions. It has three parts, slide, rule and a transparent sliding cursor. The slide rule was replaced by an electronic pocket calculator in the early 1970s.
ii. Compare 1stand 3rdgeneration computers.
| First Generation Computers | Third Generation Computers |
| First-generation computers used vacuum tubes. | Third-generation computers used IC chips. |
| Speed was slow and memory was very small. | IC chips improved the speed and memory of computers. |
| First-generation computers were very expensive and unreliable. | They are cheaper and more reliable than first-generation computers. |
| They consumed a lot of power and generated a lot of heat. | These computers consumed less electricity |
iii. Differentiate between analogue and digital computers.
| Analog Computer | Digital Computer |
| 3. These computers are often used in business, education, supermarkets etc. | 1. A digital computer accepts data in digital form. |
| 2. These are special-purpose computers. | 2. Digital computers are general purpose in use. |
| 3. These are also used in industrial units to control various processes. | 3. These computers are often used in business, education, supermarkets etc. |
| 4. Analog computers are fast in their processing but are not accurate. | 4. Digital computers are fast in their processing and are accurate. |
| 5. These computers have small memory sizes. | 5. The memory capacity is huge. |
iv. Ahmed, a class IX student is asking his father to replace his home computer CRT monitor with a LCD monitor. How will you justify his demand?
Ans: Justification of his demand:
- LCDs have uniform screen brightness and are covered with a flexible surface compared to a glass-covered CRT monitor screen.
- LCDs are flicker-free, which should reduce the risks of headaches and eye strain.
- Because LCDs are smaller than CRT monitors, LCDs require less space than CRT monitors.
- LCD also requires less energy than CRT Monitors.
v. What will happen if storage devices are removed from a computer?
Ans: Storage devices are core functions and fundamental components of computers. The Purpose of the memory device is to store the information and for the information retrieval. If storage devices are removed from a computer then it will not be possible to store the information and information retrieval.
vi. Differentiate between systems software and application software.
Ans:
| System Software | Application Software |
| System software is a collection of programs, which makes the use of computers easy and efficient. | Application software is developed for computer users to solve their problems |
| System software does not depend on application software. | Application software depends on system software. |
| Programming of system software is complex. | Programming of application software is easy. |
| A computer cannot run without system software. | A computer can easily run without application software. |
| System software do not depend on application software. | Application software is designed to accomplish tasks for specific purposes. |
vii. How can a student use a computer to improve academic performance?
Ans:
- Using computer applications increases the student’s motivation for learning Management.
- Using a computer catches the students’ attention and increases their interest in learning management.
- Using computer applications leads to the development of student’s skills.
- Using computer applications develops the students’ process of thinking critically.
- Using computer applications creates the opportunity for students to be active in class, and not passive.
viii. Give any three uses of computers in a school library.
Answer: Following are three uses of computers in a school library:
- Access to primary information sources.
- Network accessibility on Intranet and Internet.
- It has advanced search and retrieval.
- Integration with other digital libraries.
ix. Name a few household appliances in which microprocessors are used.
Answer:
- Washing machines
- Microwave cookers
- Dishwashers
- Electric kettles
- Fridges
- Remote control television
- Hairdryers
x. What tasks are performed by the operating system?
Answer: The following tasks are performed by the operating system.
- It loads programs into memory and executes them.
- It controls the operation of input/output and storage devices.
- It manages files and folders.
- It allows the creation of a password to protect computers from unauthorized use.
- It detects hardware failures and displays messages to fix them.
Write long answers to the following questions.
i. Describe the five generations of computers.
Answer:
First Generation Computers (1940 – 1956):
The following are the characteristics of first-generation computers.
- First-generation computers used vacuum tubes.
- Speed was slow and memory was very small.
- They were huge in size taking up the entire room.
- First-generation computers were very expensive and unreliable.
- They consumed a lot of power and generated a lot of heat.
- The input was based on punched cards.
- Output was obtained on printouts through the electric typewriter.
- Machine language was used in these computers.
Second Generation Computers (1956 – 1963)
The following are the characteristics of second-generation computers.
- Transistors were used instead of vacuum tubes.
- Transistors reduced the size of computers and increased the speed and memory capacity.
- Computers have become more reliable and cheaper.
- Second-generation computers used punch card readers, magnetic tapes, magnetic disks and printers.
- Assembly language was used in these computers.
- High-level programming languages, such as FORTRAN and COBOL, were introduced in this generation of computers.
Third Generation Computers (1963 — 1971):
The following are the characteristics of the third generation of computers.
- Third-generation computers used IC chips.
- IC chips improved the speed and memory of computers.
- Computers consumed less electricity and became smaller, cheaper and more reliable than second-generation computers.
- A keyboard and monitor were used with the computer.
- These computers could run different application programs at the same time.
Fourth Generation Computers (1971 – Present):
The following are the characteristics of the fourth generation of computers:
- The microprocessor was developed which resulted in the development of microcomputers.
- Fourth-generation computers are high-speed and have large storage capacity.
- Microcomputers are very small in size, very reliable, consume less power and are affordable.
- A large variety of software is available for use in microcomputers.
- An operating system having a Graphical User Interface (GUI) was developed in this generation.
- Fourth-generation computers support a large variety of portable and wireless input/output devices.
Fifth Generation Computers
The goal of the fifth generation of computers is to develop devices that can understand natural languages and have thinking power.
The following are the characteristics of the fifth generation of computers:
- Fifth-generation computers are based on Artificial Intelligence (Al).
- In the fifth generation of computers, Al will minimize the need to write programs.
- These computers will allow users to give commands in any natural language such as English.
ii. Write a note on mainframe, minicomputer and microcomputer.
Mainframe Computer:
Mainframe computers were developed in the early 1940s. A mainframe computer is large, powerful, and expensive. It can support hundreds or even thousands of users at the same time. Therefore, large organizations use these computers. They can execute more than a trillion instructions per second (TIPS). Examples of mainframe computers are IBM’s Enterprise EC12, EC 196, and HP 16500 Series.
Minicomputer:
The minicomputer was introduced in the 1960s when IC chips were introduced. A minicomputer is bigger than a microcomputer but smaller than a mainframe. These computers can execute billions of instructions per second (BIPS). Therefore, they can process more data than microcomputers. Organizations with hundreds of users, such as PIA, NADRA, police departments, and hospitals, use these computers. Examples of minicomputers are IBM System/36 and HP 3000.
Microcomputer:
Microcomputers are the smallest and most low-cost computers. These computers are most commonly used in homes and offices. Microcomputer was introduced in the 1970s when the microprocessor was developed. Microcomputers are available in various forms such as desktops, laptops and tablets. Some popular companies that manufacture microcomputers are IBM, Dell, HP, Toshiba and Acer. A microcomputer is also known as a Personal Computer or PC.
iii. Explains the basic operations of a computer.
Ans: The following four basic operations are performed by computers
- Input operation
- Processing operation
- Storage operation
- Output operation

Input Operation
A computer is a data processing machine. Users enter data and instructions into the computer through a keyboard or mouse. It can also be provided to the computer from a storage device such as a hard disk, CD or USB memory. The input data/instructions are stored in memory for further processing.
Processing Operation
The microprocessor processes data according to given instructions. It fetches data or instructions from the memory and stores them in the instruction register. The control unit decodes the instruction to determine which operation to perform. After decoding, it sends signals to other parts of the computer to execute the operation.
Storage Operation
The results produced after processing are stored in memory before they are sent to the output device or permanent storage device like a hard disk.
Output Operation
The processed results stored in memory must be output for the user to see. The control unit displays the results on the monitor or prints them on the printer. Results can also be saved on a storage device like a hard disk for future use.
iv. Write a short note on the following.
a. Hardware Engineer
b. Network Administrator
c. Database Administrator
d. Web Designer
e. Multimedia Designer
Answer:
a. Hardware Engineer:
Hardware Engineer designs and manufactures computer hardware. Their work also involves the repair and maintenance of computer hardware.
b. Network Administrator:
Network Administrators install, configure, and maintain computer networks in organizations. They assign passwords to network users. This keeps unauthorized people from accessing the network.
c. Database Administrator:
A web designer plans and creates websites. They design web pages with text, images, sound, and video clips. They also make the website interactive.
d. Web Designer:
A web designer is a person whose job is to plan and create websites. They design web pages that include text, images, sound, and video clips and makes the website interactive.
e. Multimedia Designer:
A multimedia designer presents information in an easy-to-understand and attractive way. They create digital images for animation using computer software.
v. Describe the following types of application software.
a. Productivity software
b. Business software
c. Entertainment software
d. Education software
Answer:
a. Productivity Software
Productivity software includes word-processing, spreadsheet, and database management software packages. Individuals use these software packages to speed up their daily tasks. They help people work in an organized and efficient way.
b. Business Software
Business software helps a business run more efficiently and improves productivity. Some common examples of business software include accounting, sales and marketing, inventory control, project management, and payroll software.
c. Entertainment Software
Software developed to entertain people is known as entertainment software. Video games are one of the most popular forms of entertainment software. Many games are a lot of fun to play but sometimes they can also help to improve skills such as typing or reading. The term edutainment merges games and education software into a single software. Edutainment software is used mainly for entertainment but it educates as well.
d. Education Software
Software developed for educational purposes is known as education software. A large variety of education software has been developed. Education software includes typing tutors, spelling tutors, language learning, medical and healthcare, driving test and flight simulation software, etc.
Select the best answer for the following MCQs.
i. Who invented the logarithm?
A. Blaise Pascal
B. John Napier
C. Charles Babbage
D. Herman Hollerith
ii. Which generation of the computer used Transistor?
A. 1stGeneration of Computers
B. 2nd Generation of Computers
C. 3rdGeneration of Computers
D. 4th Generation of Computers
iii. In which generation of computer Microprocessor was introduced?
A. 1stGeneration of Computers
B. 2nd Generation of Computers
C. 3rdGeneration of Computers
D. 4th Generation of Computers
iv. Which of the following Computer supports thousands of users at the same time?
A. Microcomputer
B. Minicomputer
C. Mainframe computer
D. Laptop computer
v. Who is responsible for protecting information and information systems from unauthorized people in an organization?
A. System Analyst
B. Information Security Analyst
C. Network Administrator
D. Hardware Engineer
vi. Which of the following is the fastest memory?
A. USB flash drive
B. RAM
C. ROM
D. Cache
vii. What type of software a device driver is?
A. Application software
B. Business Software
C. System software
D. Productivity Software
viii. Which of the following is a volatile memory?
A. RAM
B. ROM
C. USB flash drive
D. Hard disk
ix. Which software is distributed free of cost for a limited period as a trial version?
A. Open source software
B. Shareware
C. Freeware
D. Productivity Software
x. When were IC chips developed?
A. Early 1960s
B. Early 1970s
C. 1980s
D. 1990s
